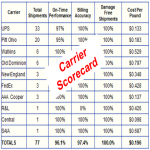
The LTL carrier scorecard with key process indicators (KPI) is an excellent tool for measuring and managing LTL performance and LTL carrier performance. The LTL carrier scorecard becomes a roadmap for driving LTL shipping improvements.
Advantages of Using an LTL Carrier Scorecard
- LTL carriers are measured objectively, rather than subjectively.
- Useful, actionable data for carrier selection and evaluation.
- Areas for improvement are quickly and easily identified.
Why Measure LTL Carrier Performance?
The old adage, “you can’t manage something you can’t” measure” definitely applies in logistics. Without measurement, shippers and logistics providers are not able to objectively analyze logistics performance. If you can’t objectively analyze performance, how will you ever improve it?
Many LTL shippers don’t use the measurements that are readily available and easy to use. These same LTL shippers are evaluating and selecting LTL carriers based on subjective criteria. Perhaps this is why, so many LTL shippers make purchasing decisions based on price alone.
There is a better way. Below is a review of LTL key process indicators and a methodology for creating an LTL carrier scorecard.
Key Process Indicators vs. Metrics
A metric is any standard of measurement (number of carriers, inventory turns, average shipment weight, etc.). A key process indicator (KPI) is a metric that you have chosen that will give an indication of your performance and can be used as a driver for improvement. In general it’s preferred to choose just a few KPIs (say 3 or 4) to focus on.
This means that while all KPIs are metrics, not all metrics are KPIs. Only the most important metrics can grow up to become KPIs.
Selecting the Right LTL KPIs
When it comes to LTL shipments, the most important attributes are 1.) On time performance, 2.) Damage, 3.) Billing accuracy, 4.) Cost.
To measure success in these four areas, a simple, transparent KPI is created for each attribute. The best KPIs for measuring these four attributes are: 1.) On time performance percentage, 2.) Damage free shipment percentage, 3.) Billing accuracy percentage, 4.) Cost per pound.
The calculation used for each of the above KPIs is described below:
On Time Performance Calculation
To calculate the on time performance KPI, simply divide the number of on time shipments by the total number of shipments.
Example: 40 on time shipments divided by 43 total shipments equals 93% on-time performance.
For the calculation, compare the transit time provided by the carrier to the actual transit time. To maintain integrity, it is important to track the actual transit time, rather than rely on the carrier’s data.
Damage Free Shipment Calculation
To calculate the damage free shipment KPI, simply divide the number of damage free shipments by the total number of shipments.
Example: 112 damage free shipments divided by 113 total shipments equals 99.1% damage free shipments.
Be sure to measure all damage not just freight claims filed. Damaged packaging, small scratches, and loose pieces are all upsetting to the receiver and the end customer so they should be documented and measured, even if there isn’t a freight claim filed.
Billing Accuracy Calculation
To calculate the billing accuracy, divide the number of correct bills by the total number of bills.
Example: 61 correct bills divided by 64 total bills equals 95% billing accuracy.
Cost Per Pound Calculation
To calculate the cost per pound KPI, take the cost of the shipment and divide it by the shipment weight (pounds).
Example: $507.34 divided by 1440 lbs. equals $0.35 cost per pound.
Cost per pound will vary between $0.06 and $0.75 with most shipments falling in the $0.22 – $0.42 range. Lower cost per pound is obviously better because it means the shipments were less expensive.
LTL Carrier Scorecard – Pulling it Altogether
To create an LTL carrier scorecard, the KPIs described above are used to populate the matrix (see LTL Carrier Scorecard graphic). The KPI information should be sorted by the carriers used. The number of shipments for each LTL carrier should also be captured on the scorecard.
Every company and shipper has different needs, so additional KPIs can be created and used to drive further improvement.
Once the scorecard is complete, the areas for improvement practically jump off the page. Shippers can use the scorecard as a starting point for driving improvement. The scorecard also is a great place to begin conversations between shippers and carriers.
Additional Reading on LTL Carrier Scorecards & LTL KPIs
Bottom line: The LTL carrier scorecard is the best way to measure and manage LTL carrier performance. The scorecard pulls together the most important LTL KPIs: on time performance, cost, freight damage and billing accuracy.